Epiretinal Membrane

What is;
It is a condition of the macula that usually appears after the age of 50. The main symptom is blurring of the central vision and distortion of images (metamorphopsia). It usually affects one eye. This membrane can grow over time, harden, and create traction, which leads to swelling of the macula. The idiopathic form, which is the most common, is not due to any disease but only to aging. However, can be secondary to certain eye diseases such as: diabetic retinopathy, posterior vitreous detachment with retinal tear, retinal detachment, trauma, inflammation, etc.
The reduction of vision acuity, due to the epiretinal membrane, is measured by checking the visual acuity and by the amount of distortion (distorted-crooked lines), with the Amsler grid.
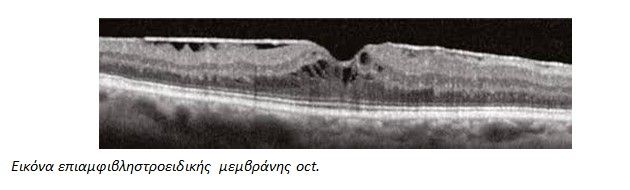
The gold standard test for diagnosing and staging the epiretinal membrane is the optical coherence tomography (OCT), which is an imaging and diagnostic method of the eye that achieves high-resolution cross-layer images of the retina without contacting the eye.
What are the symptoms of the condition?
- Blurred
- Distortion of images (straight lines appear checkered).
- Loss of central vision.
What are the causes of the disease?
The most frequent predisposing factor is the pre-existing vitreous detachment.
Other causes often include:
- Old retinal tears
- History of photocoagulation
- History of inflammatory diseases of the eyes
- Intraocular injuries, etc.
What is the treatment?
The treatment of the epiretinal membrane is surgical. It requires pars plana vitrectomy and removal of the membrane with special tools. With modern techniques, the operation now takes less than an hour with very good vision improvement results.
The timing of surgery is important. The general rule is that every symptomatic patient should be operated. The result is relative to the pre-existing visual acuity and improvement usually occurs gradually and takes time.
Are there any possible complications?
Eye infection is a very serious complication that requires urgent treatment.
There is a small risk of retinal detachment in the first months after surgery. Additionally, patients who have not undergone cataract surgery may experience an acceleration of normal cataract progression.
What are the success rates?
– 70% gradual increase in vision over one year.
– 25% stabilization of vision at the levels it was before the operation.
– 5% reduction in vision, despite the anatomical success of the operation.
Therefore, the decision to treat the condition surgically is important, as it offers a total of 95% positive results and only 5% negative results.
The postoperative goals:
- The anatomical improvement (removal of the membrane and elimination of traction-edema)
The improvement in visual acuity.
- The anatomical improvement (removal of the membrane and elimination of traction-edema)
- The improvement in visual acuity.